
The viewer spins the nosepiece to select different objective lenses. Nosepiece: A rotating turret that houses the objective lenses. Fine adjustment: Fine tunes the focus and increases the detail of the specimen. Coarse adjustment: Brings the specimen into general focus. Arm: The arm connects the body tube to the base of the microscope. Body tube (Head): The body tube connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses. Diopter Adjustment: Useful as a means to change focus on one eyepiece so as to correct for any difference in vision between your two eyes. The eyepiece usually contains a 10X or 15X power lens. Combined, they control both the focus and quantity of light applied to the specimen.Ĭondenser Focus Knob moves the condenser up or down to control the lighting focus on the specimen.Įyepiece: The lens the viewer looks through to see the specimen. Most high quality microscopes include an Abbe condenser with an iris diaphragm. It is located above the condenser and below the stage. Iris Diaphragm controls the amount of light reaching the specimen. It is located under the stage often in conjunction with an iris diaphragm. Condenser is used to collect and focus the light from the illuminator on to the specimen. Most light microscopes use low voltage, halogen bulbs with continuous variable lighting control located within the base. Illuminator is the light source for a microscope, typically located in the base of the microscope. Aperture is the hole in the stage through which the base (transmitted) light reaches the stage. The viewer is required to move the slide manually to view different sections of the specimen. Stage Clips are used when there is no mechanical stage. A mechanical stage is used when working at higher magnifications where delicate movements of the specimen slide are required. Stage is where the specimen to be viewed is placed. Coaxial focus knobs are more convenient since the viewer does not have to grope for a different knob. Increasingly, they are coaxial knobs - that is to say they are built on the same axis with the fine focus knob on the outside. Coarse and Fine Focus knobs are used to focus the microscope.

Standard objectives include 4x, 10x, 40x and 100x although different power objectives are available. The objectives are exposed and are mounted on a rotating turret so that different objectives can be conveniently selected.
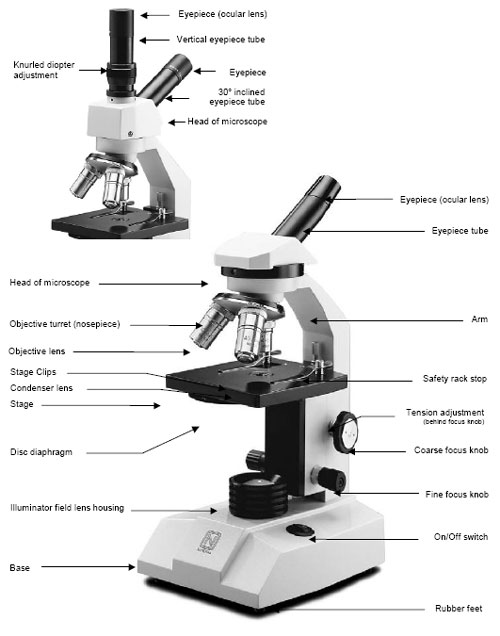

They range from 4x-100x and typically, include, three, four or five on lens on most microscopes. Objective Lenses are the primary optical lenses on a microscope. Binocular microscopes also swivel (Interpupillary Adjustment) to allow for different distances between the eyes of different individuals. The monocular (single eye usage) microscope does not need a diopter. Binocular microscope heads typically incorporate a diopter adjustment ring that allows for the possible inconsistencies of our eyesight in one or both eyes. Eyepiece Tube holds the eyepieces in place above the objective lens. Optional eyepieces of varying powers are available, typically from 5x-30x. Typically, standard eyepieces have a magnifying power of 10x. OPTICAL COMPONENTS There are two optical systems in a compound microscope: Eyepiece Lenses and Objective Lenses: Eyepiece or Ocular is what you look through at the top of the microscope. When carrying a compound microscope always take care to lift it by both the arm and base, simultaneously. Head/Body houses the optical parts in the upper part of the microscope Base of the microscope supports the microscope and houses the illuminator Arm connects to the base and supports the microscope head. STRUCTURAL COMPONENTS The three basic, structural components of a compound microscope are the head, base and arm. These key microscope parts are illustrated and explained below. However, within these two basic systems, there are some essential components that every microscopist should know and understand.

Essentially, a compound microscope consists of structural and optical components.
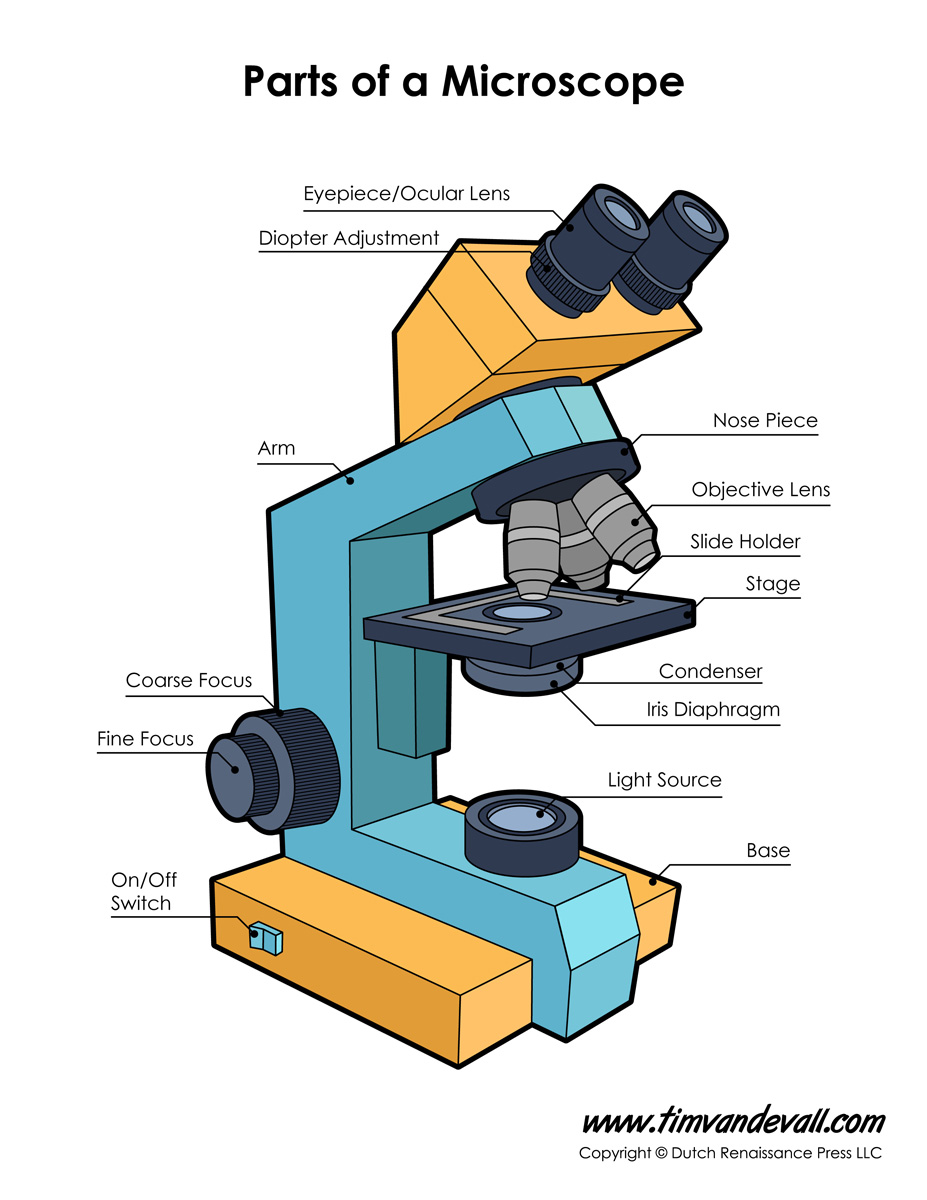
It is used to view smaller specimens such as cell structures which cannot be seen at lower levels of magnification. Compound Microscope Parts A high power or compound microscope achieves higher levels of magnification than a stereo or low power microscope.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
